 We are pleased to announce the next generation of the online resources AraPheno (https://arapheno.1001genomes.org) and the AraGWAS Catalog (https://aragwas.1001genomes.org) which has just been published in the journal Nucleic Acids Research (https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article/doi/10.1093/nar/gkz925/5603218). AraPheno is a central and manually curated repository for high-quality phenotypes for the model organism Arabidopsis thaliana. As of September 2019 AraPheno contains more than 462 publicly available phenotypes, making it the largest data resource for population-scale phenotypes in A. thaliana, by far. With this release, AraPheno has been extended to support RNA-Seq expression profiles for thousands of samples and genes.
We are pleased to announce the next generation of the online resources AraPheno (https://arapheno.1001genomes.org) and the AraGWAS Catalog (https://aragwas.1001genomes.org) which has just been published in the journal Nucleic Acids Research (https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article/doi/10.1093/nar/gkz925/5603218). AraPheno is a central and manually curated repository for high-quality phenotypes for the model organism Arabidopsis thaliana. As of September 2019 AraPheno contains more than 462 publicly available phenotypes, making it the largest data resource for population-scale phenotypes in A. thaliana, by far. With this release, AraPheno has been extended to support RNA-Seq expression profiles for thousands of samples and genes.
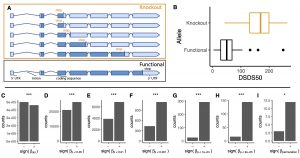
The AraGWAS Catalog is a central and manually curated resource of genetic associations for all available phenotypes from AraPheno. All GWAS results in the AraGWAS Catalog are re-computed using a standardized and permutation-based GWAS pipeline on an identical release of genomic data. This will not only enable and facilitate comparative analysis between GWAS results but also the detection of pleiotropic effects. The AraGWAS Catalog has been extensively updated to also provide more detailed information about associations and its allelic distributions. For the first time, the AraGWAS Catalog also includes novel associations between knockout (KO) mutations and population-scale phenotypes from AraPheno. Loss-of-function mutations can be an important source of genetic variation in the evolution of plant traits and we found an overrepresentation of KO-trait relationships toward smaller trait values.
All results and new features can be found in our Nucleic Acids Research publication:
M Togninalli, Ü Seren, J.A. Freudenthal, J.G. Monroe, D Meng, M Nordborg, D Weigel, K Borgwardt, A Korte, and D.G. Grimm, “AraPheno and the AraGWAS Catalog 2020: a major database update including RNA-Seq and knockout mutation data for Arabidopsis thaliana.” Nucleic Acids Research (NAR), 2019
